Differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
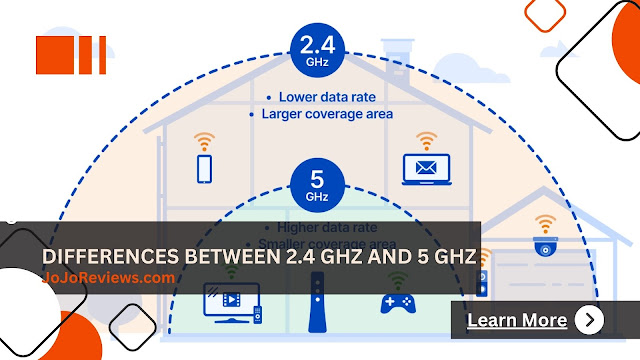
However, they have distinct characteristics that affect network quality. WiFi technology has a long history, and it's no surprise that the 2.4 GHz network, which is the standard for consumer WiFi, has become increasingly crowded and susceptible to interference. To address this issue, internet service providers offer 5 GHz connectivity, also known as dual connection. Each frequency band, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, has its own advantages, strengths, and weaknesses, including speed, range, and more. To delve deeper into the differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi, let's explore several key distinctions.
1. WiFi Network Frequencies
The first difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi lies in the radio wave frequencies used to transmit WiFi signals. The 2.4 GHz WiFi frequency refers to the range of radio wave frequencies between 2.4 gigahertz (GHz), covering frequencies from around 2,400 to 2,483.5 GHz. On the other hand, the 5 GHz WiFi frequency refers to the range of radio wave frequencies between 5,150 and 5,825 GHz. This range encompasses higher frequencies compared to 2.4 GHz WiFi.
2. WiFi Network Range
The second difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi can be observed in the range of the WiFi network. The 2.4 GHz WiFi has a wider range than 5 GHz WiFi. The 2.4 GHz WiFi signal has better penetration capabilities through walls and physical objects. This means that the 2.4 GHz WiFi signal can cover a larger area within an environment, even through physical barriers like walls. On the other hand, 5 GHz WiFi has a more limited range compared to 2.4 GHz WiFi. The 5 GHz WiFi signal has lower penetration capabilities through walls and physical objects. As a result, the range of 5 GHz WiFi tends to be shorter, and its performance can be more affected by physical barriers like walls.
3. WiFi Network Density
The difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi can be observed in terms of network density. The network density of 2.4 GHz WiFi can be higher compared to 5 GHz WiFi. This is due to two main factors:
- Firstly, the 2.4 GHz frequency is more commonly used and supported by most WiFi devices, including older devices.
- Secondly, 2.4 GHz WiFi has a more limited channel range, specifically 13 overlapping channels. This means there are limitations on the number of channels available for use, resulting in more networks sharing the same channel in a given area.
On the other hand, the network density of 5 GHz WiFi is usually lower compared to 2.4 GHz WiFi. The 5 GHz frequency is used more sparingly and is only supported by newer WiFi devices. Additionally, 5 GHz WiFi has a wider channel range, including non-overlapping channels.
4. WiFi Network Speed
The next difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi is based on network speed. Generally, 2.4 GHz WiFi has lower data transfer speeds compared to 5 GHz WiFi. This is due to the narrower bandwidth of the 2.4 GHz frequency. 2.4 GHz WiFi uses channels with a bandwidth of 20 MHz, and some devices may support channels with 40 MHz or 80 MHz bandwidth, but this can cause interference with other channels. The average data transfer speeds of 2.4 GHz WiFi range from 150 Mbps to 600 Mbps, depending on device specifications and network configurations. On the other hand, 5 GHz WiFi generally offers higher data transfer speeds compared to 2.4 GHz WiFi. The higher frequency range of 5 GHz WiFi allows for wider bandwidth. 5 GHz WiFi uses channels with bandwidths of 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, or 160 MHz, enabling faster data transfer speeds. The average data transfer speeds of 5 GHz WiFi can reach several hundred Mbps to several Gbps.
5. Device Compatibility
The final difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi lies in device compatibility.
For 2.4 GHz WiFi:
- 2.4 GHz WiFi has broader compatibility with various types of devices. This is because the 2.4 GHz frequency has been widely used for a long time and is supported by most existing WiFi devices.
- Devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, IoT devices, and consumer electronics generally support connections to 2.4 GHz WiFi networks.
- Additionally, older or budget devices tend to only support 2.4 GHz WiFi.
On the other hand, for 5 GHz WiFi:
- 5 GHz WiFi has more limited compatibility compared to 2.4 GHz WiFi. Although an increasing number of devices support 5 GHz WiFi, some devices still only support 2.4 GHz WiFi or have limited support for 5 GHz WiFi.
- In general, newer and premium devices are more likely to have support for 5 GHz WiFi. For example, most smartphones, laptops, and newer electronic devices support 5 GHz WiFi.
- However, older devices or devices with budget constraints may not have the ability to connect to 5 GHz WiFi networks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 2.4 GHz WiFi
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of 2.4 GHz WiFi:
Advantages of 2.4 GHz WiFi
- Wider range: The 2.4 GHz WiFi signal has better penetration capabilities through walls and physical objects, allowing it to cover a larger area. The signal can reach up to 36 meters indoors and 92 meters outdoors.
- Better compatibility: Almost all modern WiFi devices support connections to 2.4 GHz networks, ensuring compatibility across a wide range of devices.
- Lower interference: Since the 2.4 GHz frequency is more commonly used, areas with many WiFi networks tend to experience higher interference on the 5 GHz frequency. In some cases, this can result in a more stable connection on the 2.4 GHz frequency.
Disadvantages of 2.4 GHz WiFi
- Lower data transfer speeds: 2.4 GHz WiFi generally has lower data transfer speeds compared to 5 GHz WiFi due to its narrower bandwidth.
- High frequency congestion: Due to the widespread use of the 2.4 GHz frequency, there can be many WiFi networks and other devices using the same frequency in the surrounding area. This can lead to high network density and interference, which can affect the performance and speed of the user's WiFi connection.
- Vulnerability to interference: 2.4 GHz WiFi signals are more susceptible to interference from other electronic devices using the same or nearby frequencies, such as microwaves, cordless phones, or Bluetooth devices. Such interference can disrupt signal quality and data transfer speeds.
- Limited channels: The 2.4 GHz frequency range is limited to 13 overlapping channels. If there are many WiFi networks around using the same channel, it can impact the performance and stability of the user's WiFi connection.
Advantagesand Disadvantages of 5 GHz WiFi
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of 5 GHz WiFi:
Advantages of 5 GHz WiFi
- Higher data transfer speeds: 5 GHz WiFi generally offers higher data transfer speeds compared to 2.4 GHz WiFi. The higher frequency range of 5 GHz allows for faster data transfer.
- Lower frequency congestion: Since the 5 GHz frequency is used less extensively compared to the 2.4 GHz frequency, there is less interference and disruption from other WiFi networks or devices using the same frequency. This results in a more stable connection and consistent speeds.
- Wider channel availability: 5 GHz WiFi utilizes more non-overlapping channels compared to 2.4 GHz WiFi. This provides more channel options to reduce interference and improve signal quality.
Disadvantages of 5 GHz WiFi
- Limited range: 5 GHz WiFi signals have a shorter range compared to 2.4 GHz WiFi signals. The 5 GHz signal has lower penetration capabilities through walls and physical objects. Therefore, 5 GHz WiFi tends to have a more limited range.
- Limited device compatibility: While most modern WiFi devices support connections to 5 GHz networks, older devices may not have support for the 5 GHz frequency. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure device compatibility with 5 GHz WiFi before connecting.
- Susceptibility to physical interference: 5 GHz WiFi signals are more vulnerable to interference from physical objects such as walls, doors, and other household appliances. This can result in decreased signal quality and data transfer speeds if there are many obstacles between the WiFi device and the router.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi is crucial for optimizing network performance and choosing the appropriate frequency for specific needs. Factors such as frequency, range, network density, speed, and device compatibility should be taken into consideration when selecting the WiFi frequency that best suits your requirements.

Post a Comment for "Differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz"